Botulinum Toxin Surgery
Botulinum toxin is a protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, and is extremely neurotoxic.When introduced intravenously in monkeys, type A of the toxin exhibits an LD50 of 40-56 ng, type C1 around 32 ng, type D 3200 ng, and type E 88 ng, rendering the above types some of the most powerful neurotoxins known. Popularly known by one of its trade names, Botox or Dysport, it is used for various cosmetic and medical procedures.
BoNT is broken into 7 neurotoxins (labeled as types A, B, C [C1, C2], D, E, F, and G), which are antigenically and serologically distinct but structurally similar. Human botulism is caused mainly by types A, B, E, and (rarely) F. Types C and D cause toxicity only in animals.
The various botulinum toxins possess individual potencies, and care is required to assure proper use and avoid medication errors. Recent changes to the established drug names by the FDA were intended to reinforce these differences and prevent medication errors. The products and their approved indications include the following:
Injections are performed with a Teflon-coated, 24-gauge needle connected to an electromyographic (EMG) machine. Those muscles with highest clinical and EMG activity are injected. Usually, 2-4 separate muscles are injected in 1 session and, in larger muscles, 2-4 sites per muscle are injected.
No general consensus exists among users of BoNT regarding the need for EMG guidance while injecting the compound for cervical dystonia. EMG guidance, however, is helpful, particularly in obese patients whose neck muscles cannot adequately be palpated.
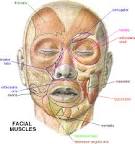
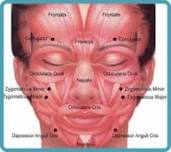
Identifying the specific muscles involved in cervical dystonia prior to the injection is important. Those most commonly injected are the sternocleidomastoid, trapezius, splenius capitis, and levator scapulae muscles. An EMG study of 100 patients found that 2 or 3 muscles commonly are abnormal. Eighty-nine percent of patients with rotating torticollis had involvement of the ipsilateral splenius capitis and contralateral sternocleidomastoid with or without the additional involvement of the contralateral splenius capitis. Patients with laterocollis had ipsilateral sternocleidomastoid, splenius capitis, and trapezius involvement, while retrocollis was produced by bilateral splenius capitis activity.
Beneficial effect from toxin injection usually is apparent in 7-10 days. Maximum response from the toxin is reached in approximately 4-6 weeks and lasts for an average of 12 weeks. Injections usually are repeated every 3-4 months.
Most studies have reported side effects in 20-30% of patients per treatment cycle. The incidence of adverse effects varies based on the dosage used (ie, the higher the dose, the more frequent the adverse effects); however, Jankovic and Schwartz reported that incidence of complications was not related to the total dose of BoNT used.9 Women and patients who received injections into the sternocleidomastoid muscles had significantly higher rates of complications.
Dysphagia has been the most prevalent significant complication and most probably is related to diffusion of the toxin into nearby pharyngeal muscles. In the study by Comella and colleagues, 33% of patients receiving their first dose of botulinum toxin experienced dysphagia.10 This complication most commonly occurs with injections of the sternocleidomastoid and can be reduced significantly when the dose of toxin administered is 100 U or les
Botulinum toxin has been used since 1980 to treat many muscle disorders such as lazy eye and uncontrolled blinking. It was pioneered by dermatologic surgeons for cosmetic use in 1987.
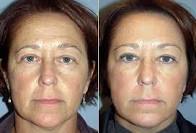
Botulinum toxin type A is specifically indicated for the lines between the eyebrows, and it also can be effectively used for "off-label" indications in other facial areas.
Once the muscle is weakened and relaxed, it cannot contract. Since there is no way to make the undesirable facial expression, the lines gradually smooth out from disuse, and new creases are prevented from forming. Other muscles such as those needed to raise the eyebrows are not affected, so a natural expression is maintained. For optimal results, botulinum toxin therapy may be used in combination with other cosmetic skin procedures such as chemical peels, laser resurfacing, and dermal fillers. Combination therapy also can help prevent the formation of new lines and wrinkles. Botulinum toxin is less useful for the smile lines around the mouth because muscle action in this area is needed for important functions such as eating and talking.
Botulinum toxin has been used since 1980 to treat many muscle disorders such as lazy eye and uncontrolled blinking. It was pioneered by dermatologic surgeons for cosmetic use in 1987.
Botulinum toxin type A is specifically indicated for the lines between the eyebrows, and it also can be effectively used for "off-label" indications in other facial areas.
Once the muscle is weakened and relaxed, it cannot contract. Since there is no way to make the undesirable facial expression, the lines gradually smooth out from disuse, and new creases are prevented from forming. Other muscles such as those needed to raise the eyebrows are not affected, so a natural expression is maintained. For optimal results, botulinum toxin therapy may be used in combination with other cosmetic skin procedures such as chemical peels, laser resurfacing, and dermal fillers. Combination therapy also can help prevent the formation of new lines and wrinkles. Botulinum toxin is less useful for the smile lines around the mouth because muscle action in this area is needed for important functions such as eating and talking.
Some women also report that their personal relationships improve after Botox treatment because they can no longer make automatic frowning movements with their face and appear to be happier and more well rested which puts others at ease.
People who are bothered by excessive hydrosis or sweating may also benefit greatly from Botox injections. Excessive sweating in the underarm area and on the palms of the hands can be a tremendously embarrassing problem and Botox treatment can remedy this situation and greatly improve self esteem.
In addition a few patients report a flu-like condition with body aches and headache that may last for several days. Botox treatments will usually be effective immediately and will likely last for several months but the patient may have to return for additional cosmetic Botox injections after a few months to maintain the effects.
To find a plastic surgeon who performs this procedure, visit the online referral service of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). ASPS, founded in 1931, is the largest plastic surgery organization in the world and the foremost authority on cosmetic and reconstructive plastic surgery. All ASPS physician members are certified by the American Board of Plastic Surgery (ABPS) or the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada.















Introduction
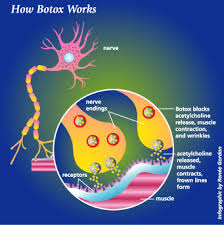
Botulinum toxin (abbreviated either as BTX or BoNT) is produced by Clostridium botulinum, a gram-positive anaerobic bacterium. The clinical syndrome of botulism can occur following ingestion of contaminated food, from colonization of the infant gastrointestinal tract, or from a wound infection.BoNT is broken into 7 neurotoxins (labeled as types A, B, C [C1, C2], D, E, F, and G), which are antigenically and serologically distinct but structurally similar. Human botulism is caused mainly by types A, B, E, and (rarely) F. Types C and D cause toxicity only in animals.
The various botulinum toxins possess individual potencies, and care is required to assure proper use and avoid medication errors. Recent changes to the established drug names by the FDA were intended to reinforce these differences and prevent medication errors. The products and their approved indications include the following:
- OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox, Botox Cosmetic)
- Botox - Cervical dystonia, severe primary axillary hyperhidrosis, strabismus, blepharospasm
- Botox Cosmetic - Moderate-to-severe glabellar lines
- AbobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport) - Cervical dystonia, moderate-to-severe glabellar lines
- IncobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin) - Cervical dystonia, blepharospasm
- Rimabotulinumtoxin B (Myobloc) - Cervical dystonia
Procedure
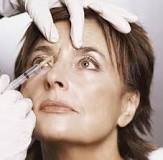
Treatment dosages of BoNT-A in the United States have been reported to range from 100-300 U per patient. In a double-blind, placebo-controlled study, Poewe and colleagues demonstrated that magnitude and duration of improvement were greatest after injections of 1000 U of Dysport, but the injections caused significantly more adverse effects.8 The researchers recommended a lower starting dose of 500 U of Dysport (1 U of BoNT-A = 3 U of Dysport). One hundred U of toxin per mL of preservative-free normal saline are commonly used.Injections are performed with a Teflon-coated, 24-gauge needle connected to an electromyographic (EMG) machine. Those muscles with highest clinical and EMG activity are injected. Usually, 2-4 separate muscles are injected in 1 session and, in larger muscles, 2-4 sites per muscle are injected.
No general consensus exists among users of BoNT regarding the need for EMG guidance while injecting the compound for cervical dystonia. EMG guidance, however, is helpful, particularly in obese patients whose neck muscles cannot adequately be palpated.
Identifying the specific muscles involved in cervical dystonia prior to the injection is important. Those most commonly injected are the sternocleidomastoid, trapezius, splenius capitis, and levator scapulae muscles. An EMG study of 100 patients found that 2 or 3 muscles commonly are abnormal. Eighty-nine percent of patients with rotating torticollis had involvement of the ipsilateral splenius capitis and contralateral sternocleidomastoid with or without the additional involvement of the contralateral splenius capitis. Patients with laterocollis had ipsilateral sternocleidomastoid, splenius capitis, and trapezius involvement, while retrocollis was produced by bilateral splenius capitis activity.
Beneficial effect from toxin injection usually is apparent in 7-10 days. Maximum response from the toxin is reached in approximately 4-6 weeks and lasts for an average of 12 weeks. Injections usually are repeated every 3-4 months.
Complications
Neck weakness, dysphagia, and local pain at the injection site are the most commonly reported side effects. Other adverse effects (eg, local hematoma, generalized fatigue, lethargy, dizziness, dry mouth, dysphonia, flulike syndrome, pain in neighboring muscles) also have been reported.Most studies have reported side effects in 20-30% of patients per treatment cycle. The incidence of adverse effects varies based on the dosage used (ie, the higher the dose, the more frequent the adverse effects); however, Jankovic and Schwartz reported that incidence of complications was not related to the total dose of BoNT used.9 Women and patients who received injections into the sternocleidomastoid muscles had significantly higher rates of complications.
Dysphagia has been the most prevalent significant complication and most probably is related to diffusion of the toxin into nearby pharyngeal muscles. In the study by Comella and colleagues, 33% of patients receiving their first dose of botulinum toxin experienced dysphagia.10 This complication most commonly occurs with injections of the sternocleidomastoid and can be reduced significantly when the dose of toxin administered is 100 U or les
History
Justinus Kerner described botulinum toxin as a "sausage poison" and "fatty poison", because the bacterium that produces the toxin often caused poisoning by growing in improperly-handled or -prepared meat products. It was Kerner, a physician, who first conceived a possible therapeutic use of botulinum toxin and coined the name botulism (from Latinbotulus meaning "sausage"). In 1897, Emile van ErmengemClostridium botulinum to be the producer of botulinum toxin. In 1928, P. Tessmer Snipe and Hermann Sommer for the first time purified the toxin. In 1949, Burgen's group discovered that botulinum toxin blocks neuromuscular transmission identified the bacterium
What is botulinum toxin?
Botulinum toxin type A and botulinum toxin type B are purified substances, derived from a bacteria, that block muscular nerve signals. Injecting very small amounts into specific facial muscles blocks the muscle's impulse. This temporarily weakens the muscle and diminishes the unwanted lines.Botulinum toxin has been used since 1980 to treat many muscle disorders such as lazy eye and uncontrolled blinking. It was pioneered by dermatologic surgeons for cosmetic use in 1987.
Botulinum toxin type A is specifically indicated for the lines between the eyebrows, and it also can be effectively used for "off-label" indications in other facial areas.
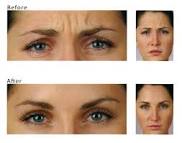
Once the muscle is weakened and relaxed, it cannot contract. Since there is no way to make the undesirable facial expression, the lines gradually smooth out from disuse, and new creases are prevented from forming. Other muscles such as those needed to raise the eyebrows are not affected, so a natural expression is maintained. For optimal results, botulinum toxin therapy may be used in combination with other cosmetic skin procedures such as chemical peels, laser resurfacing, and dermal fillers. Combination therapy also can help prevent the formation of new lines and wrinkles. Botulinum toxin is less useful for the smile lines around the mouth because muscle action in this area is needed for important functions such as eating and talking.
Are there any side effects?
Side effects are generally minimal, temporary, and typically relate to the local injection. Soreness or mild bruising, while uncommon, may occur around the injection site. Makeup may be applied after the treatment, but care should be taken to avoid pressing or massaging the area for several hours. A temporary headache is not uncommon after injections in the forehead area, especially after the first treatment. In rare instances, patients may develop weakness of the neighboring muscles leading to a temporary droopy brow or eyelid. All of these possible effects are mild, reversible, and self-limiting.What is botulinum toxin?
Botulinum toxin type A and botulinum toxin type B are purified substances, derived from a bacteria, that block muscular nerve signals. Injecting very small amounts into specific facial muscles blocks the muscle's impulse. This temporarily weakens the muscle and diminishes the unwanted lines.Botulinum toxin has been used since 1980 to treat many muscle disorders such as lazy eye and uncontrolled blinking. It was pioneered by dermatologic surgeons for cosmetic use in 1987.
Botulinum toxin type A is specifically indicated for the lines between the eyebrows, and it also can be effectively used for "off-label" indications in other facial areas.
Once the muscle is weakened and relaxed, it cannot contract. Since there is no way to make the undesirable facial expression, the lines gradually smooth out from disuse, and new creases are prevented from forming. Other muscles such as those needed to raise the eyebrows are not affected, so a natural expression is maintained. For optimal results, botulinum toxin therapy may be used in combination with other cosmetic skin procedures such as chemical peels, laser resurfacing, and dermal fillers. Combination therapy also can help prevent the formation of new lines and wrinkles. Botulinum toxin is less useful for the smile lines around the mouth because muscle action in this area is needed for important functions such as eating and talking.
Are there any side effects?
Side effects are generally minimal, temporary, and typically relate to the local injection. Soreness or mild bruising, while uncommon, may occur around the injection site. Makeup may be applied after the treatment, but care should be taken to avoid pressing or massaging the area for several hours. A temporary headache is not uncommon after injections in the forehead area, especially after the first treatment. In rare instances, patients may develop weakness of the neighboring muscles leading to a temporary droopy brow or eyelid. All of these possible effects are mild, reversible, and self-limiting.Who Benefits from Botox?
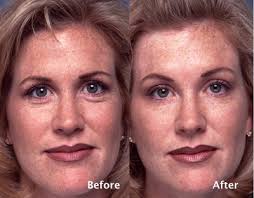
Women who have mild to moderate frown lines on the forehead, between the eyes and around the mouth may benefit from cosmetic Botox treatments. It may temporarily reduce the ability to wrinkle the skin and may eliminate the appearance of lines on the face.Some women also report that their personal relationships improve after Botox treatment because they can no longer make automatic frowning movements with their face and appear to be happier and more well rested which puts others at ease.
People who are bothered by excessive hydrosis or sweating may also benefit greatly from Botox injections. Excessive sweating in the underarm area and on the palms of the hands can be a tremendously embarrassing problem and Botox treatment can remedy this situation and greatly improve self esteem.
Botox Side Effects
Though Botox injections are generally considered to be safe, it does have a number of side effects that should be understood. Botox does not typically require a recovery period but some patients will experience localized pain and irritation at the injection site.In addition a few patients report a flu-like condition with body aches and headache that may last for several days. Botox treatments will usually be effective immediately and will likely last for several months but the patient may have to return for additional cosmetic Botox injections after a few months to maintain the effects.
Botulinum Toxin
The cosmetic form of botulinum toxin is a popular non-surgical injection that temporarily reduces or eliminates frown lines, forehead creases, crows feet near the eyes and thick bands in the neck. The toxin blocks the nerve impulses, temporarily paralyzing the muscles that cause wrinkles while giving the skin a smoother, more refreshed appearance. Studies have also suggested that botulinum toxin is effective in relieving migraine headaches, excessive sweating and muscle spasms in the neck and eyes.To find a plastic surgeon who performs this procedure, visit the online referral service of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). ASPS, founded in 1931, is the largest plastic surgery organization in the world and the foremost authority on cosmetic and reconstructive plastic surgery. All ASPS physician members are certified by the American Board of Plastic Surgery (ABPS) or the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada.






0 comments:
Post a Comment